English grammar can be challenging, even for native speakers. Mistakes in grammar can change the meaning of a sentence, create confusion, or simply leave a less-than-favorable impression. This blog post will cover some of the most common English grammar mistakes and provide tips on how to avoid them.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
1. Subject-Verb Agreement Errors
The Mistake: One of the most frequent errors in English grammar is the mismatch between the subject and verb in a sentence. This usually happens when the subject is singular, but the verb is plural, or vice versa.
Example:
- Incorrect: The team are winning.
- Correct: The team is winning.
Why It Happens: Confusion often arises when the subject of the sentence is a collective noun (like «team,» «group,» or «family»). These words may represent a group of people, but they are grammatically singular.
How to Avoid It: Always identify whether the subject is singular or plural, and match the verb accordingly. A good practice is to simplify the sentence to see if the verb matches the subject.

Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
2. Misuse of Apostrophes
The Mistake: Apostrophes are often used incorrectly, particularly in forming possessives and contractions.
Example:
- Incorrect: Its a beautiful day. (This is wrong because «its» is possessive, but the context requires a contraction of «it is.»)
- Correct: It’s a beautiful day.
Why It Happens: People often confuse «its» (possessive form of «it») with «it’s» (a contraction for «it is» or «it has»). Similarly, they might misuse apostrophes in plurals (e.g., «apple’s» instead of «apples»).
How to Avoid It: Remember that apostrophes indicate possession or replace missing letters in contractions. For possessives, if the noun is singular, the apostrophe comes before the «s» (e.g., «the cat’s toy»). For plural nouns that end in «s,» the apostrophe comes after the «s» (e.g., «the cats’ toys»). Contractions, like «it’s» for «it is,» always need an apostrophe.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
3. Confusion Between Homophones
The Mistake: Homophones are words that sound the same but have different meanings and spellings. Common homophones that are frequently confused include «they’re,» «their,» and «there»; «your» and «you’re»; and «to,» «two,» and «too.»
Example:
- Incorrect: There going to bring their books with them.
- Correct: They’re going to bring their books with them.
Why It Happens: Because homophones sound the same, it’s easy to mix them up in writing, especially when typing quickly.
How to Avoid It: Take your time when writing, and think about the meaning of the word you want to use. Proofread your work to catch any homophone mistakes. If you’re unsure, look up the words to ensure you’re using the correct one.

Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
4. Incorrect Use of Commas
The Mistake: Commas are often either overused or underused, which can lead to confusing or run-on sentences.
Example:
- Incorrect: I went to the store and I bought apples oranges and bananas.
- Correct: I went to the store, and I bought apples, oranges, and bananas.
Why It Happens: The rules around commas can be complex, leading to uncertainty about when to use them.
How to Avoid It: Learn the basic rules of comma usage. For instance, use commas to separate items in a list, after introductory phrases, or to set off nonessential information. Reading your sentences out loud can also help; if you naturally pause, you may need a comma.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
5. Misplaced Modifiers
The Mistake: A misplaced modifier is a word or phrase that is incorrectly separated from the word it describes, causing confusion.
Example:
- Incorrect: Running quickly, the finish line was soon crossed.
- Correct: Running quickly, the athlete soon crossed the finish line.
Why It Happens: Writers may place modifiers too far from the word they are describing, leading to unclear or awkward sentences.
How to Avoid It: Place the modifier as close as possible to the word it describes. This helps to keep the sentence clear and easy to understand.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
6. Incorrect Pronoun Usage
The Mistake: Pronouns must agree in number and gender with the nouns they replace. Incorrect pronoun usage can make sentences confusing or grammatically incorrect.
Example:
- Incorrect: Every student must bring their pencil.
- Correct: Every student must bring his or her pencil.
Why It Happens: The use of «they» as a singular pronoun has become common in informal contexts, but it can lead to grammatical errors.
How to Avoid It: Ensure that your pronouns match the nouns they refer to in both number and gender. If the gender is unknown or irrelevant, consider restructuring the sentence to avoid the problem (e.g., «All students must bring their pencils»).
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
7. Overuse of Passive Voice
The Mistake: The passive voice occurs when the subject of the sentence is acted upon rather than performing the action. While passive voice is not always incorrect, its overuse can make writing weak and unclear.
Example:
- Incorrect: The ball was thrown by the boy.
- Correct: The boy threw the ball.
Why It Happens: Writers might use passive voice to avoid mentioning who is performing the action, or simply out of habit.
How to Avoid It: Prefer the active voice in most cases, as it makes sentences clearer and more direct. If you find that a sentence feels weak or indirect, check if it’s in passive voice and see if it can be revised.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
8. Run-On Sentences and Comma Splices
The Mistake: Run-on sentences occur when two or more independent clauses are connected without proper punctuation. A comma splice is a specific type of run-on where two independent clauses are joined by a comma without a conjunction.
Example:
- Incorrect: I love writing it is my favorite hobby.
- Correct: I love writing. It is my favorite hobby.
Why It Happens: Writers may create run-ons and comma splices when they try to combine closely related ideas into a single sentence without proper punctuation.
How to Avoid It: Use a period, semicolon, or a comma with a coordinating conjunction (like «and,» «but,» or «so») to separate independent clauses. Breaking up complex ideas into separate sentences can also improve clarity.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
9. Inconsistent Tense Usage
The Mistake: Switching between past, present, and future tenses in a sentence or paragraph can confuse the reader.
Example:
- Incorrect: She walks to the store and bought milk.
- Correct: She walked to the store and bought milk.
Why It Happens: Writers sometimes switch tenses unintentionally, especially when describing events that happened in sequence.
How to Avoid It: Maintain a consistent tense throughout your sentences and paragraphs. If you start describing events in the past tense, continue using the past tense unless there’s a clear reason to change.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
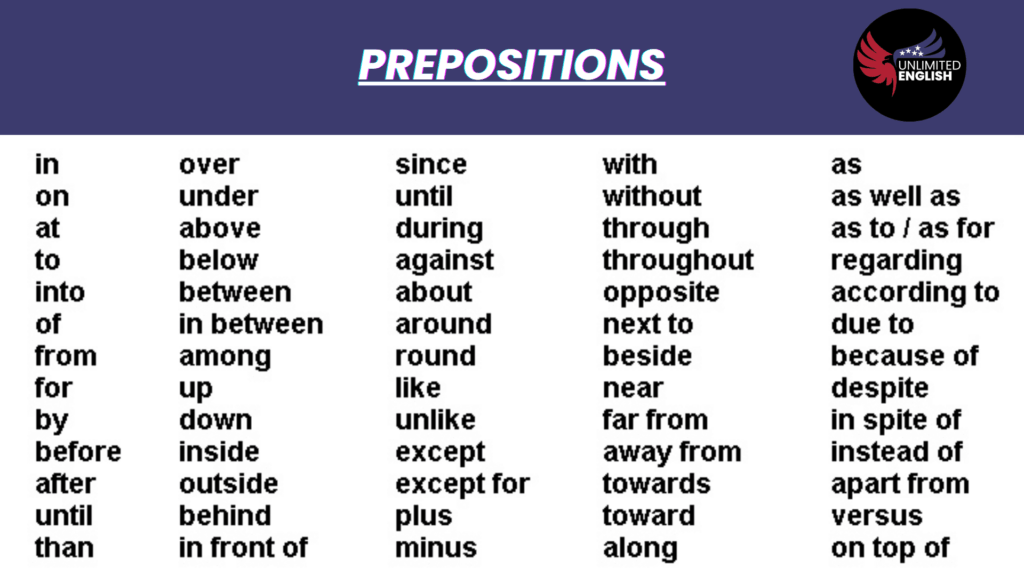
10. Incorrect Use of Prepositions
The Mistake: Prepositions can be tricky because their use often depends on idiomatic expressions rather than strict rules.
Example:
- Incorrect: She is good in math.
- Correct: She is good at math.
Why It Happens: Different languages and dialects use prepositions differently, which can lead to mistakes for non-native speakers.
How to Avoid It: Learn common prepositional phrases and practice using them correctly. When in doubt, consult a dictionary or grammar resource to ensure you’re using the right preposition.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
11. Improper Use of Articles
The Mistake: Articles («a,» «an,» and «the») are often misused, especially by those whose first language doesn’t include articles.
Example:
- Incorrect: She has dog.
- Correct: She has a dog.
Why It Happens: Articles can be confusing because they are used in different ways depending on the context.
How to Avoid It: Understand the basic rules: «a» and «an» are used with singular, non-specific nouns, while «the» is used with specific nouns. Practice by reading and listening to native English to get a feel for how articles are used.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
12. Spelling Mistakes
The Mistake: Spelling errors are common, especially with words that sound similar but are spelled differently or words that are irregular.
Example:
- Incorrect: They’re going to loose the game.
- Correct: They’re going to lose the game.
Why It Happens: Spelling mistakes often occur because of the irregularities in English spelling or simply due to typing errors.
How to Avoid It: Use spell-check tools, but don’t rely on them entirely, as they may not catch every mistake. Proofreading your work or having someone else review it can help catch errors that spell-check might miss. Reading more can also help reinforce correct spelling patterns in your mind.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
13. Overgeneralization of Rules
The Mistake: Writers may overgeneralize the rules of capitalization, such as capitalizing every word in a sentence or capitalizing common nouns that don’t require it.
Example:
- Incorrect: The Students attended The Lecture on Science.
- Correct: The students attended the lecture on science.
Why It Happens: Sometimes, people assume that important-sounding words should be capitalized or that every word in a title must be capitalized, even when it’s not necessary.
How to Avoid It: Understand that only proper nouns (specific names of people, places, organizations, etc.), the first word of a sentence, and certain titles should be capitalized. Common nouns, unless they are part of a proper noun or at the beginning of a sentence, should not be capitalized.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
14. Inconsistent Use of Titles and Headings
The Mistake: When writing titles or headings, some writers inconsistently apply capitalization rules, either using too much or too little capitalization.
Example:
- Incorrect: The effects Of Climate Change On Agriculture.
- Correct: The Effects of Climate Change on Agriculture.
Why It Happens: Confusion often arises because different style guides (such as APA, MLA, or Chicago) have different rules for capitalizing titles and headings.
How to Avoid It: Familiarize yourself with the capitalization rules of the style guide you’re following. Typically, major words (nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs) are capitalized, while minor words (articles, conjunctions, prepositions) are not, unless they are the first or last word in the title.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
15. Lack of Attention to Detail
The Mistake: Writers may simply overlook capitalization errors due to carelessness or lack of attention to detail.
Example:
- Incorrect: he went to Paris for the summer.
- Correct: He went to Paris for the summer.
Why It Happens: When typing quickly or focusing on the content rather than the mechanics of writing, it’s easy to miss capitalization errors.
How to Avoid It: Make a habit of proofreading your work, specifically checking for capitalization errors. Reading your writing out loud or using tools like grammar checkers can help identify mistakes.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
16. Influence of Texting and Informal Writing
The Mistake: With the rise of texting and informal communication, many people have become accustomed to not capitalizing at all or using lowercase letters for everything.
Example:
- Incorrect: i went to the park yesterday.
- Correct: I went to the park yesterday.
Why It Happens: In informal settings like texting, capitalization is often ignored to save time or because it’s seen as unnecessary. This habit can carry over into more formal writing.
How to Avoid It: Be mindful of the context in which you’re writing. While it may be acceptable to use all lowercase in a text message, formal writing requires proper capitalization. Practice writing in full sentences with correct capitalization, even in casual settings, to reinforce the habit.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
17. Uncertainty About Proper Nouns
The Mistake: Writers sometimes struggle to distinguish between proper nouns (which should be capitalized) and common nouns (which should not).
Example:
- Incorrect: My friend works at the Hospital.
- Correct: My friend works at the hospital.
Why It Happens: Proper nouns refer to specific names of people, places, or things, while common nouns refer to general categories. However, the distinction isn’t always clear, especially when the noun feels important or unique.
How to Avoid It: Ask yourself if the noun is a specific name or title. If it is, capitalize it. If it’s a general term, it should remain lowercase. When in doubt, consult a dictionary or style guide.

Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
18. Influence of Other Languages
The Mistake: For non-native English speakers, the capitalization rules of their first language might interfere with their English writing.
Example:
- Incorrect: My Mother is a Doctor. (in some languages, capitalization of titles or familial terms is common)
- Correct: My mother is a doctor.
Why It Happens: Different languages have different rules for capitalization. For example, in German, all nouns are capitalized, which can lead to confusion for German speakers writing in English.
How to Avoid It: Be aware of the differences in capitalization rules between your first language and English. Regular practice and reading in English can help internalize the correct rules.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
19. Misunderstanding of the Rules Around Capitalizing After Colons
The Mistake: Writers often get confused about whether to capitalize the first word after a colon.
Example:
- Incorrect: He had one goal: To win the race.
- Correct: He had one goal: to win the race.
Why It Happens: The rules for capitalizing after a colon vary depending on the context. In general, the first word after a colon is not capitalized unless it is a proper noun or the start of a complete sentence.
How to Avoid It: Remember that if the phrase following the colon is a complete sentence, you may capitalize the first word. If it’s a fragment or a list, do not capitalize unless it’s a proper noun.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
20. Inconsistent Capitalization in Compound Proper Nouns
The Mistake: When dealing with compound proper nouns (names of people, places, organizations, etc. that are made up of more than one word), writers sometimes capitalize inconsistently.
Example:
- Incorrect: the University of california, Berkeley
- Correct: The University of California, Berkeley
Why It Happens: The confusion often arises when only part of the compound noun seems important or when the rules around capitalizing each word aren’t clear.
How to Avoid It: In a compound proper noun, each major word should be capitalized. This includes the first word and any subsequent nouns, adjectives, or verbs. Prepositions and conjunctions are usually not capitalized unless they are the first word in the name.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
21. Inconsistent Use of Capitalization in Abbreviations
The Mistake: Writers sometimes struggle with capitalizing abbreviations, especially when those abbreviations are commonly spelled out in full or used in different contexts.
Example:
- Incorrect: The usa is a large country.
- Correct: The USA is a large country.
Why It Happens: When abbreviations become common, their usage can become inconsistent, especially in informal writing. People may forget that the abbreviation represents a proper noun or formal term.
How to Avoid It: Always capitalize abbreviations of proper nouns or formal terms. If you’re unsure, look up the standard usage in a reliable source.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
22. Influence of Branding and Creative Choices
The Mistake: In some contexts, especially in branding and marketing, companies or individuals may choose to use lowercase letters for stylistic reasons, even for proper nouns or at the beginning of sentences. This can influence how people write in other contexts.
Example:
- Incorrect: I just got a new iphone.
- Correct: I just got a new iPhone.
Why It Happens: Brand names like “iPhone” or “eBay” use non-standard capitalization, and this creative choice can sometimes confuse writers, leading them to improperly capitalize other words.
How to Avoid It: When writing formally or outside of a brand-specific context, stick to standard capitalization rules. Be aware of the distinction between a brand’s stylistic choices and correct grammar.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
23. Errors in Capitalizing Directions and Regions
The Mistake: Writers sometimes incorrectly capitalize cardinal directions (north, south, east, west) or fail to capitalize them when they should be.
Example:
- Incorrect: I’m traveling to the West of France.
- Correct: I’m traveling to the west of France.
Why It Happens: The confusion arises because directions (north, south, east, west) are not capitalized when they refer to direction, but they are capitalized when they refer to specific regions (e.g., “the South” in the U.S.).
How to Avoid It: Capitalize directions only when they refer to specific regions or are part of a proper noun (e.g., «the West Coast,» «South America»). Do not capitalize when simply indicating direction (e.g., «drive east,» «north of the river»).
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
24. Improper Capitalization in Quoted Material
The Mistake: Writers may struggle with whether to capitalize the first word in a quote, especially if the quote is embedded within a sentence.
Example:
- Incorrect: She said that “the party was amazing.”
- Correct: She said that “the party was amazing.”
Why It Happens: The rules for capitalizing quoted material depend on whether the quote is a complete sentence or a fragment. This distinction can lead to confusion.
How to Avoid It: If the quote is a complete sentence, capitalize the first word. If the quote is a fragment or part of your sentence, do not capitalize the first word unless it is a proper noun.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
25. Incorrect Capitalization in Professional Titles
The Mistake: Writers often incorrectly capitalize professional titles, either by overcapitalizing or failing to capitalize when appropriate.
Example:
- Incorrect: The President of the company will speak today.
- Correct: The president of the company will speak today.
Why It Happens: Confusion arises when a title is used generically versus when it is used as part of a person’s specific title.
How to Avoid It: Capitalize titles only when they are used before a person’s name (e.g., «President Smith») or when referring to a specific office (e.g., «the President of the United States»). Do not capitalize when using the title generically (e.g., «the president of the company»).
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
26. Overcapitalization Due to Emphasis
The Mistake: Sometimes, writers capitalize words to emphasize them, which is incorrect in formal writing.
Example:
- Incorrect: This is a Very Important Message.
- Correct: This is a very important message.
Why It Happens: People might capitalize words for emphasis, thinking it adds importance or weight to the text.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
How to Avoid It: Use italics or bold text for emphasis in informal writing. In formal writing, rely on strong word choices and sentence structure to convey importance, rather than capitalization.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
27. Mistakes in Capitalizing Titles in Different Languages
The Mistake: When writing titles in languages other than English, writers might incorrectly apply English capitalization rules.
Example:
- Incorrect: Les Misérables by Victor Hugo (French titles often capitalize only the first word and proper nouns).
- Correct: Les misérables by Victor Hugo.
Why It Happens: Different languages have different rules for capitalizing titles, and applying English rules to titles in other languages can lead to errors.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
How to Avoid It: When writing titles in other languages, research the correct capitalization rules for that language. For instance, in French, only the first word and proper nouns are capitalized unless the title begins with a definite article, which might then be capitalized.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
28. Errors in Capitalizing Historical Events and Periods
The Mistake: Writers sometimes incorrectly capitalize historical events, periods, or eras, either by overcapitalizing or undercapitalizing.
Example:
- Incorrect: The Renaissance period was marked by great cultural change.
- Correct: The Renaissance period was marked by great cultural change.
Why It Happens: Confusion can arise because the names of some historical periods and events are capitalized, while generic terms for time periods are not.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
How to Avoid It: Capitalize specific names of historical periods, eras, and events (e.g., «the Renaissance,» «World War II»). Do not capitalize when referring to generic time periods (e.g., «the medieval period,» «the early 20th century»).
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
29. Capitalization in Legal and Technical Writing
The Mistake: In legal and technical writing, certain terms are often capitalized to denote specific concepts or parties, but this practice can lead to overcapitalization in other contexts.
Example:
- Incorrect: The Plaintiff argued that the Defendant was at fault.
- Correct: The plaintiff argued that the defendant was at fault.
Why It Happens: Legal and technical documents often capitalize terms for clarity, but this habit can spill over into other writing where it is unnecessary.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
How to Avoid It: Understand the context in which you are writing. If you are drafting a legal or technical document, follow the specific capitalization rules for that field. In general writing, avoid unnecessary capitalization.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
30. Failure to Capitalize Religions, Deities, and Religious Terms
The Mistake: Writers may fail to capitalize the names of religions, deities, religious figures, and important religious terms, or they may overcapitalize generic religious terms.
Example:
- Incorrect: He is a follower of christianity.
- Correct: He is a follower of Christianity.
Why It Happens: The distinction between proper nouns (which should be capitalized) and common nouns can cause confusion, especially in religious contexts.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
How to Avoid It: Capitalize the names of religions (e.g., «Christianity,» «Islam»), deities (e.g., «God,» «Allah»), and specific religious figures (e.g., «Jesus,» «Muhammad»). Do not capitalize common religious terms unless they begin a sentence or are part of a proper noun.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
31. Mistakes in Capitalizing Seasons
The Mistake: Writers often incorrectly capitalize the names of seasons, either by overcapitalizing them or failing to capitalize them when they are part of a title or specific event.
Example:
- Incorrect: I love the Winter.
- Correct: I love the winter.
Why It Happens: Seasons are commonly capitalized in error because they are often perceived as important or distinct.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
How to Avoid It: Do not capitalize the names of seasons (e.g., «spring,» «summer,» «fall,» «winter») unless they are part of a title or specific event name (e.g., «Winter Olympics»).

Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
32. Errors Due to Auto-Correct and Predictive Text
The Mistake: Auto-correct and predictive text features in word processors and mobile devices can sometimes lead to incorrect capitalization.
Example:
- Incorrect: the meeting is scheduled for Tomorrow.
- Correct: The meeting is scheduled for tomorrow.
Why It Happens: Auto-correct features might capitalize words based on past behavior or assumptions, leading to errors in formal writing.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
How to Avoid It: Review your writing carefully for any capitalization errors introduced by auto-correct. Disable automatic capitalization features if they frequently cause issues, or adjust the settings to better match your writing style.
Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
As we saw previously, by being mindful of these additional reasons, you can further refine your understanding and application of proper capitalization in your writing. Regular practice, proofreading, and consulting reliable grammar resources can help you avoid these mistakes and improve the overall clarity and professionalism of your work.

Common English Grammar Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
If you would like to improve on these areas, we can help you. At Unlimited English, our English professors are certified native English speakers with years of experience. It does not matter what your English level is. You can either fill out the newsletter or contact us on Whatsapp for our free 30 minute interview. We look forward to hearing from you!

